Theory Z:
Theory Z is a Japanese consensus management style base on the assumption that
Theory Z is a Japanese consensus management style base on the assumption that
- Employees want to build cooperative relationships with their employers, peers, and other employees in the firms.
- They require high degree of support in the form of secure employment and facilities for development of multiple skills through training and job rotation.
- They value family life, culture and traditions, and social institutions as much as material success.
- They have well-developed sense of dedication, moral obligation, and self-discipline.
- They can make collective decisions through consensus.
It was introduced by the author William Ouchi.
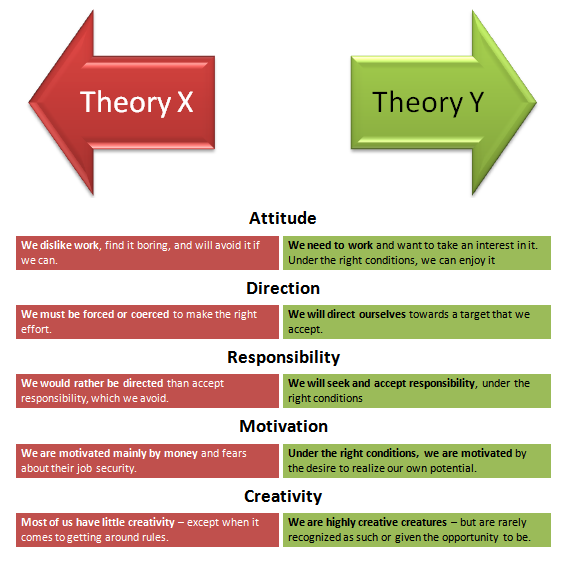
Lets compare theory Z with theory X and theory Y
Job Design:
Work arrangement or rearrangement aimed at reducing or overcoming job dissatisfaction and employee alienation arising from repetitive and mechanistic tasks. Through job design, organizations try to raise productivity levels by offering non-monetary rewards such as greater satisfaction from a sense of personal achievement in meeting the increased challenge and responsibility of one's work.
- Job enlargement,
- job enrichment,
- job rotation
- job simplification
are the various techniques used in a job design exercise.
Importance of Job Design:
Job design is a very important function of staffing. If the jobs are designed properly, then highly efficient managers will join the organisation. They will be motivated to improve the productivity and profitability of the organisation. However, if the jobs are designed badly, then it will result in absenteeism, high labor turnover, conflicts, and other labor problems.
Factors Affecting Job Design
1. Proper scope of job
The scope of the job should be proper. If the scope is narrow (less), then the job will not be challenging. It will not give an opportunity for development. The manager will not get satisfaction after completing an easy job. If the scope of the job is very wide, then the manager will not be able to handle it properly. This will cause stress, frustration and loss of control. Therefore, scope of the job must be balanced and proper.
2. Full-time challenge of the job
The job should be so challenging that it takes up the full-time and effort of the manager. So, the service of the manager must be fully utilized If not, the manager will have a lot of free time. He will use this free time to interfere in the work of his subordinates. This will cause problems and conflicts because subordinates do not like unnecessary interference from their superiors.
3. Managerial skills
The skills of the manager should be considered before designing his job. All managers do not have equal skills. So jobs should be designed after considering the skills of the manager. So, a manager having a high level of skill should be given very challenging jobs while a manager having a low level of skill should be given fewer challenging jobs. Jobs must be made flexible so that it can be changed according to the skills of the manager.
4. Organisation's requirements
Jobs must be designed according to the requirements of the organisation. We cannot use the same job design for all organisations.
5. Individual likes and dislikes
People have different likes and dislikes. Some people like to work alone while some people prefer to work in groups. Some people want to do only planning and decision making while other people like to implement these plans and decision. So, individual likes and dislikes must be considered while designing the job.
6. Organisational structure
Organisational structure also affects the job design. Individual jobs must fit into the organisation's structure.
7. Technology
The level of technology used by the organisation also affects the job design. An organisation having a high level of technology will have different job designs compared to an organisation having a low level of technology.